|
First, benefits of strapless
HRMs include eliminating the need for
constant cleaning of the chest strap,
removing the sense of poor body image
putting on a chest strap has for some
overweight students, and taking away
the need to change the battery in the
strap. Second, is what I call the "myth
of age inappropriateness." Although
it may be true that students under the
age of 14 may not benefit from training
in a Target Heart Rate Zone, that does
not mean we should not introduce the
concept or teach its use. Some have
suggested that "Intensity"
(one of the FITT principals) is better
taught using the perceived exertion
scale, but I have found that belief
is not necessarily accurate in practice.
Teaching the perceived exertion scale
as a means of determining intensity
or effort of physical activity can sometimes
be difficult with students of elementary
school age. Because the scale runs from
1-20 some students have a tough time
grasping the concept. This difficulty
may be due to the lack of a tactile
connection or a concrete learning tool
for students to connect with. The abstractness
of the perceived exertion scale concept
suggest it might be better left to older
elementary school or middle school students,
although I utilize it in grades 4-6
as a precursor to HRM use. Strapless
HRMs and Target Heart Rate (THR) provide
students with a tactile connection to
their body and intensity that the perceived
exertion scale cannot. I've observed
a light come on with some students (who
previously struggled with perceived
exertion) when taught intensity using
HRMs. The "cool factor" also
plays some role here. Students are actually
paying attention more because of the
HRM use. Myth busted!
Curriculum Connections
Content Vocabulary is a concept often
used with other subject areas and underutilized
with many in physical education. By
using the FITT principals, physical
educators can provide additional content
vocabulary with a lifetime wellness
focus. Two of these principals, TIME
and INTENSITY, can be taught in some
detail using strapless HRMs, including
concrete learning experiences. TIME
is a great theme because most strapless
HRMs have both a stop watch and countdown
timer on them. Utilizing logs to write
down daily time spent in activity, and
using the watch to determine time in
activity, can also provide an interdisciplinary
connection of reading and writing with
TIME (a math objective on standardized
tests).
Making a connection with a classroom
teacher and adding graphs to this activity
will incorporate several more math objectives
to a single theme, in addition to encouraging
collegiality. Using the stop watch to
provide lap times for the mile, having
students analyze those lap times, and
then creating a strategy for future
improvements will also provide a connection
to higher order thinking skills (Blooms
Taxonomy). Therefore, INTENSITY is not
the only reason to purchase HRMs, just
the main one.
 Another
interdisciplinary connection is to use
EFFORT with the K-3 group, and make
the transference to INTENSITY by introducing
synonyms/antonyms at the 3rd-4th grade
level. This is another Standardized
Assessment Literacy Skill. Write down
EFFORT and INTENSITY on a white board,
connect them with arrows, and then write
Synonyms as an off shoot (see photo).
This aids students in acquiring content
specific vocabulary, while also making
the connection to classroom learning.
Another math connection can be made
by teaching estimated average heart
rate when using INTENSITY. Another
interdisciplinary connection is to use
EFFORT with the K-3 group, and make
the transference to INTENSITY by introducing
synonyms/antonyms at the 3rd-4th grade
level. This is another Standardized
Assessment Literacy Skill. Write down
EFFORT and INTENSITY on a white board,
connect them with arrows, and then write
Synonyms as an off shoot (see photo).
This aids students in acquiring content
specific vocabulary, while also making
the connection to classroom learning.
Another math connection can be made
by teaching estimated average heart
rate when using INTENSITY.
After learning the Median (or middle
heart rate taken during class), students
can learn to estimate an average. Median,
Average, and Estimation are all math
objectives. Additionally, daily writing
down this average in their logs can
be a great way to interconnect the disciplines
and help students make the connection.
Communicating this information to other
teachers in those grades utilizes this
concept and can also provide a concrete
learning situation that students sometimes
lack in the classroom, thus reaching
more learning types such as the kinesthetic
learner.
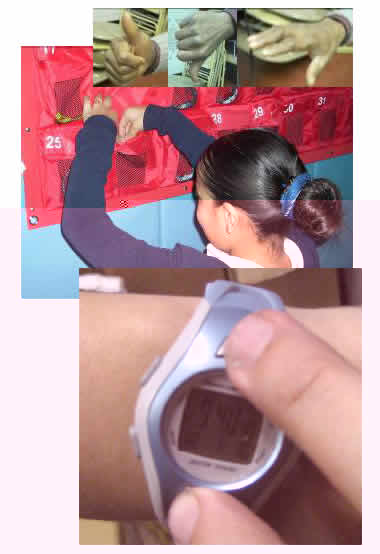
Management Tips with SHRMs
Immediately engrave numbers on the HRMs
upon receiving them. To help with maintenance
issues, initiate a system of keeping
track of those that are working and
those that are not. Next, place the
HRMs in a pocket organizer with mesh
see-through pockets, like this one that
is found in Sportime. Assign a numbered
HRM to each student in each class. At
the beginning of class call out the
HRM number, and ask students to retrieve
their HRM accordingly (one at a time).
They must wait their turn if someone
is at the station. After students have
been assigned a number (and they remember
it), they can line up as they come in
and get them one at a time. End the
period putting the HRMs away by following
the same procedure. The mesh pockets
helps you see that all the HRMs are
in their place before each class leaves.
 As a personal preference, I use Excel
to track student HRM use, HRM inventory,
and maintenance logs. This makes it
easy to set up one class with HRM numbers
and then copy and paste that column
to the rest of the classes, deleting
those HRMs not in use because of reduced
numbers of students. Using a PDA to
display the spreadsheet helps me stay
close to the action. Student helpers
are also utilized to track student HRM
use once the procedure has been taught.
This helps provide incentive for students
and encourages a student directed environment.
As a personal preference, I use Excel
to track student HRM use, HRM inventory,
and maintenance logs. This makes it
easy to set up one class with HRM numbers
and then copy and paste that column
to the rest of the classes, deleting
those HRMs not in use because of reduced
numbers of students. Using a PDA to
display the spreadsheet helps me stay
close to the action. Student helpers
are also utilized to track student HRM
use once the procedure has been taught.
This helps provide incentive for students
and encourages a student directed environment.
When using Target Heart Rate, students
below their THR put their thumb or first
finger up to denote the need to use
more intensity and put their thumb down
if they need to work less intensely.
A hand indicting "safe" means
they are in their THR zone.
Some strapless HRMs can also determine
how many calories are burned; however,
this topic is probably best left to
middle and high school students.
 Strapless
HRM Recommendations Strapless
HRM Recommendations
As with most things, the cheapest strapless
HRMs are just that, "Cheep,"
and may not live up to the quality standards
necessary for use in schools. Leaning
more toward the moderately priced strapless
HRMs may provide both the feature set
and durability required for daily use.
Another consideration is battery changing
ability. Make sure to ask whether the
battery can be changed or not. This
will add years to their shelf life.
There are several manufacturers of quality
strapless HRMs, with MIO and Reebok
leading the way. Recently, Ekho has
entered the strapless game; however,
at the time I was writing this article
Ekho was not yet shipping them. Accusplit
also makes a strapless HRM, but I have
not had a chance to evaluate them. Of
the many that I have tried and used,
the Reebok CardioSport 10 works the
best with students in the elementary
setting. They both fit better and seem
to more consistently record younger
age (grade 3) student's heart rate than
the MIO Select Sport.
Conclusion
Strapless HRMs are a wonderful starting
tool for the elementary physical educator
to break the barrier for using HRMs
with their students. They not only add
the interdisciplinary connections for
students and incorporate content vocabulary,
but also add the WOW factor for students.
Even though it might not be recommended
that you use the HRMs and Target Heart
Rate to train younger students, the
overall impact of their use on your
physical education program warrants
their use.
References
*Physical
Education for Lifelong Fitness: The
Physical Best Teacher's Guide; NASPE,
Second Edition, Human Kinetics 2005.
Resources
http://www.humankinetics.com/physicalbest/
: Physical Best resource books
http://www.sportime.com/:
Wall Organizer
http://www.heartratemonitorsusa.com/Pages/Mio/mio-all.html:
MIO Select Sport
|



